

The green color is reflected and perceived by the observer’s eye.Elizabeth Johnson and Juhong Christie Liu Behavior of Light
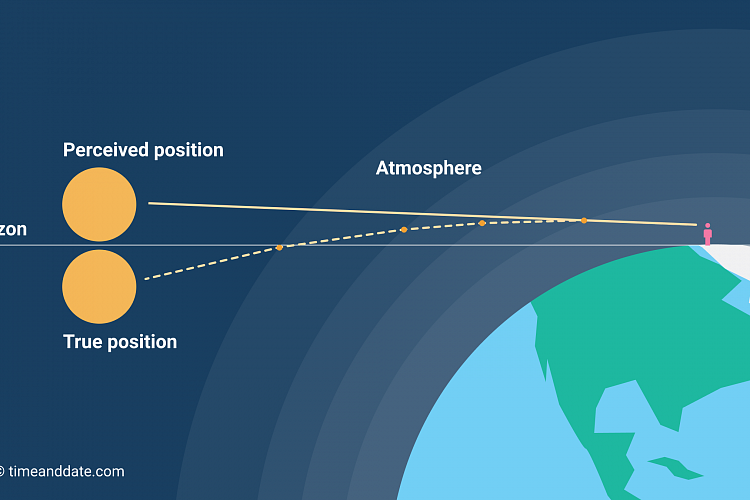
For instance, the leaf absorbs all the frequencies of light except for green. An object that appears with a particular color means that the object absorbs most of the frequencies and reflects only the color of the object. Selective absorption describes the tendency of an object to absorb specific frequencies of light. However, when an object absorbs all the components of light, it appears black. When an object reflects all the components of light, it appears white. White light is composed of different components of a spectrum: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet (ROYGBIV). If light is not transmitted, it may have been reflected or absorbed.Ībsorption of light occurs when light strikes a material, and the energy that it carries is absorbed by the atoms of the material and is converted into thermal energy. Transparent and translucent materials transmit light, but opaque materials do not. The extent of the transmission of light depends on the type of the material the light strikes. But, in physics, light can refer to any kind of electromagnetic wave: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, or gamma rays. Without it, we’d be in complete darkness. Light moves as a wave, bouncing off objects so we can see them. Visible light is the reason we are able to see anything at all. For instance, an incoming light will just pass through a glass window as transmitted light. Transmission is the passing of light through a material without being absorbed. A lower refractive index means the light travels faster, and its direction changes less upon entering a medium. A higher refractive index means the light propagates slower, and its direction changes more upon entering a medium. Refractive index describes how light propagates through a medium. On the other hand, when light travels from a medium with a high refractive index to a medium with a lower refractive index, it speeds up and refracts away from the normal line.The light ray that is entering a different medium is called the incident ray while the bent ray is called the refracted ray. When light travels from a medium with a low refractive index to a medium with a higher refractive index, it slows down and refracts closer to the normal line.

Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and waterwaves. Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. This phenomenon can be described using light rays. Reflection occurs when light bounces back as it hits a reflecting surface, such as a mirror.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
